ENVIRONMENT
Environmental Stewardship
BNSF strives to minimize our impact on the environment and to provide transportation solutions that contribute to the long-term sustainability of our customers and the communities in which we live and operate.
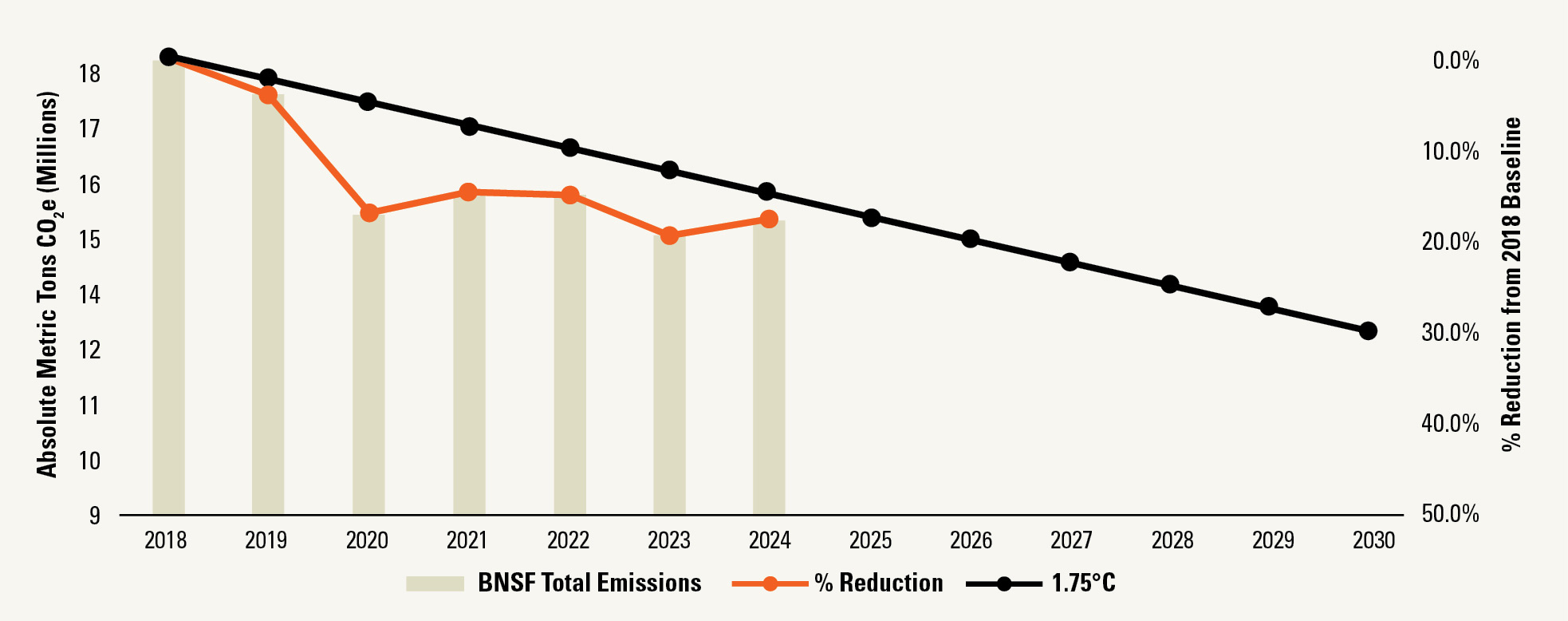
A Commitment to Reducing Carbon Emissions
BNSF set a science-based target that was reviewed, validated and approved by the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi). BNSF is committed to reducing absolute scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions, as well as the well-to-wheel GHG emissions associated with our locomotives, by 30% by 2030 (from a baseline year of 2018). BNSF plans to achieve our goal in two primary ways: by continuing to improve the fuel-efficiency of our locomotives and through the increased utilization of renewable fuels. To track our progress, BNSF compiles an annual emissions inventory following the GHG Protocol that is validated by an independent third party.


Testing Low-Carbon Fuels
In 2024, we continued testing a B20/R80 blend of fuel, which is a mixture of 20% biodiesel and 80% renewable diesel. By working with our locomotive manufacturing partners and the other railroads, we hope to increase the amount of biodiesel and renewable diesel fuels we can use to operate our locomotives, which would translate into significant carbon intensity and emission reductions for our fleet. Initial testing indicates up to 10% biodiesel and up to 50% renewable diesel can be used in our locomotives. We anticipate continued testing will push those percentage blends higher going forward.
Strengthening Our Tier 4 Fleet
BNSF continues to invest in Tier 4 locomotives, the newest and cleanest-burning locomotives in North America. For nine years, we have acquired Tier 4s, which are designed to reduce criteria pollutant emissions by 70% over standard locomotives. We currently have 360 Tier 4 Units, and 65% of our fleet is Tier 3 or better.
Increasing Fuel Efficiency
BNSF is increasing the fuel efficiency of our operations, with systems and initiatives including:
Energy Management Systems (EMS) – More than 4,000 locomotives have been equipped with EMS, such as Trip Optimizer, which allows the throttle and dynamic brakes to be controlled automatically. EMS factors the train makeup (length, weight and horsepower), track geometry, grade, curvature and speed restrictions to determine the most fuel-efficient way to operate the train across a territory while maintaining appropriate train handling.
Automatic Engine Stop/Start System (AESS) – More than 99% of our active locomotive fleet is AESS-equipped. AESS automatically shuts down a locomotive that is idling to minimize wasted fuel and eliminate unnecessary emissions. It then automatically restarts the locomotive if needed for power or necessary for the health of the engine.
Horsepower Per Trailing Ton (HPT) Reduction – Reducing the effort required to move the weight of a train, measured in Horsepower Per Trailing Ton (HPT), is another effective method to improve fuel efficiency. Practices implemented to minimize HPT include reducing excess horsepower; implementing speed-based throttle limiting to reduce fuel consumption at higher speeds; and isolating, or potentially shutting down, engines when a train has more locomotives than it needs for a given segment of its route.

Ensuring Adaptation and Resilience
Addressing Weather Related Service Interruptions
Stormwater in Urban Areas
Many of our railroad bridges were the first elements of infrastructure over 100 years ago in today's urban areas. Increased impervious surfaces due to urbanization surrounding our rail has reduced natural water infiltration upstream, causing increased volumes to drain through our railway. Additionally, we're monitoring for changes in our climate that may cause increased frequency and severity of rain events.
As our neighboring communities continue to grow and our system receives significant rainfall, BNSF focuses on adaptation and resilience of our stormwater infrastructure and systems operations. For each new or replacement bridge project, we conduct hydraulic analyses to assess flood impacts and size our bridges, culverts and track elevation appropriately.
Wildfires
BNSF has had wildfire response plans and equipment positioned throughout our system to protect our critical infrastructure for many years. With an increase in wildfire risk both in frequency and severity, our wildfire program has been expanded significantly. Today, we have more than 50 wildfire response tank cars and infrastructure protection trailers along our network. We remove trees and brush surrounding critical infrastructure to eliminate wildfire fuel. We also have developed Infrastructure Wildfire Protection plans for BNSF’s critical bridges, tunnels and snowsheds.

Sustainable Solutions for Customers
Helping to Reduce Customer Carbon Emissions
By using rail to transport goods, our customers are able to reduce their environmental impact while remaining competitive in the market. Rail, in fact, is the most environmentally efficient mode of surface transportation. Consider: railroads handle 40% of the nation’s long-distance freight volume, yet account for only 0.5% of total U.S. GHG emissions and only 1.8% of the transportation related emission sources, according to the U.S. EPA. According to the AAR, if 10% of the freight shipped by the largest trucks were moved by rail instead, greenhouse gas emissions would fall by nearly 20 million tons annually.

Collaborating with Customers to Promote Sustainability
BNSF works with customers on sustainable innovation end markets through our Sustainable Freight Leadership Council (SFLC). The SFLC brings together thought leaders from several industries to build insights and alignment on shared actions to reduce carbon emissions and create more sustainable supply chains.

Celebrating Sustainability
With the BNSF Sustainability Awards, we annually recognize customers who work with us to make their operations more sustainable. Winners are recognized in categories including Investments in Circular Economy Infrastructure, Supply Chain Efficiencies and Sustainable Technology Implementation.
Winners of the 2024 BNSF Sustainability Awards:
ABF Freight
Again Technologies
Buzzi Unicem USA
C.H. Robinson
COSCO Shipping Lines
Darling Ingredients
Diamond Green Diesel
EMR/Northern Metal Recycling
Estes Express Lines
HF Sinclair
Kimberly-Clark Corporation
Nelson & Fort Sheppard Transload
OOCL (USA)
RPMG
The Delong Co.
Valero Energy Corporation
Vestas
Supporting a Circular Economy
BNSF is helping to support new sustainable business markets built around the circular economy, where materials are perpetually reused in closed-loop supply chains and upcycled into higher-value goods. We provide sustainable supply chain solutions for enterprises involved in plastics recycling, low-carbon steel manufacturing, renewable fuels and other emerging markets.
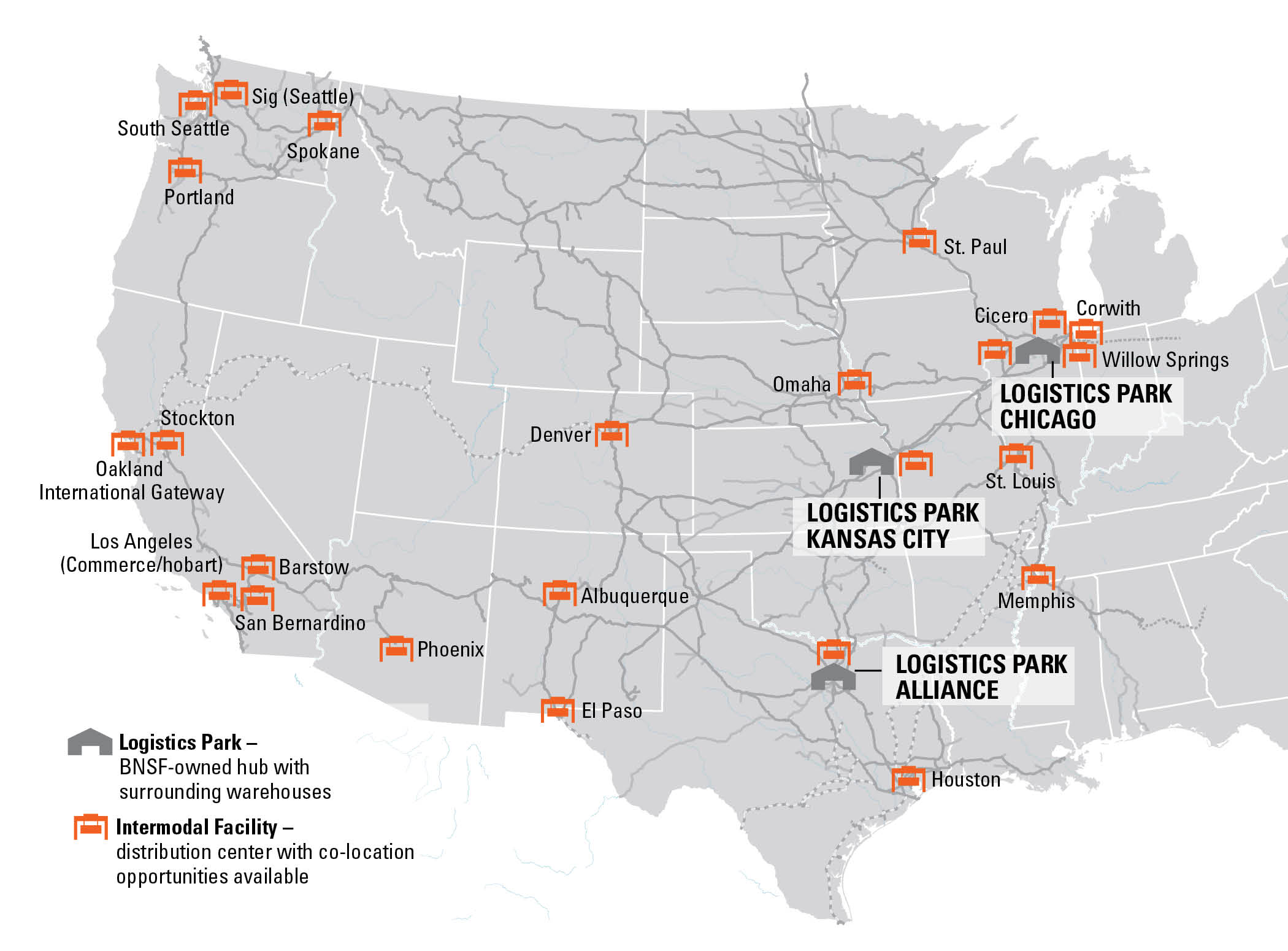
Co-Locating at Logistics Parks and Logistics Centers
BNSF customers enjoy sustainability, operational and logistical efficiency advantages by co-locating at BNSF Logistics Parks or Logistics Centers. BNSF Logistics Parks are facilities anchored by a BNSF intermodal hub and surrounded by distribution centers to provide streamlined supply chain solutions for intermodal customers. By providing the setup for customers to operate in close quarters with us, we optimize the operating footprint and limit the transportation emissions required between intermodal and distribution activities. Co-locating at these facilities gives customers direct access to BNSF services and reduces the number of truck miles driven on public roads.
At BNSF Logistics Centers, we invest directly in the development of new facilities and sites in under-serviced, strategic and primarily end-user markets to provide customers a low-carbon solution for moving their carloads. BNSF Logistics Centers serve customers with direct-rail service in multi-customer, multi-commodity business parks that enable us to meet customers where they need efficient transportation solutions most.
Logistics Parks and Intermodal Hubs
Logistics Centers
Enhancing Efficiency with Intermodal Facilities
With 27 facilities in 14 states, BNSF has the industry’s largest network of intermodal hubs, connecting consumer goods to most U.S. markets. In 2024, 5.3 million intermodal shipments were transported on our rail lines instead of over the nation’s congested highways.

BNSF continuously looks for ways to increase efficiency and reduce our operational carbon footprint with the use of leading-edge equipment and technology at our intermodal hubs, including:
- Wide-span electric cranes that produce zero emissions and reduce the number of diesel-powered hostlers required.
- Battery-electric hostlers, forklifts and drayage trucks.
- Real-Time Inventory: A combination of data sources is used to simultaneously verify and update inventory operating systems.
- Automated yard checks that utilize image analytics and machine learning.
- Remote cranes: “Wireless” remote cranes operate at Logistics Park Chicago (LPC). This remote capability improves productivity and safety.
- Automated Gate Systems (AGS) to speed entry and reduce truck idling on entering intermodal facilities.
- Load Plan Optimization: By using an AI-based algorithm that creates a load plan for an outbound train in seconds, we can ensure the right containers and trailers are located where they need to be on the production tracks, minimizing the overall distance our hostler drivers need to travel.
Developing an Innovative New Facility
In 2024, BNSF continued development of the 4,500-acre Barstow International Gateway (BIG). BIG will be a uniquely integrated operation, consisting of a rail yard, intermodal facility and warehouses for transloading freight from international containers to domestic containers. The facility will allow, for the first time, the direct transfer of containers from ships at the Ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach to trains headed to BNSF’s mainline. Containers will be processed using zero- and near-zero emission cargo-handling equipment. BIG has the potential to significantly improve network fluidity and efficiency, meaningfully reduce carbon emissions and create thousands of jobs.

Advanced Energy Innovation
In 2024, BNSF’s Advanced Energy Innovation team continued to explore decarbonization solutions including assessing:
- Battery-electric locomotives
- Hydrogen fuel cell locomotives
- Hybrid locomotives
- Hybrid rubber-tired gantry cranes
- Zero-emission solutions for cargo handling
- Solar power and microgrid technologies for facility resiliency and expense reduction
Supporting Innovative Locomotive Development
BNSF continues to explore the suitability of hybrid locomotives, whereby a battery will be added to a standard locomotive to improve fuel efficiency through the capture and re-use of “free energy” from regenerative braking.
Implementing Facility Electrification
BNSF is implementing next-generation battery-electric and hybrid-powered cargo-handling equipment at intermodal facilities on the West Coast and in the Pacific Northwest. Electric cargo-handling equipment operates more quietly, more efficiently and more cleanly than traditional diesel machines while reducing impacts on the work environment and surrounding communities.
Our Stockton yard is the first fully electric hostler facility in the United States, with 21 hostlers and a hybrid-electric rubber-tired gantry crane, which reduces emissions by 90%. The facility also has a 0.75 mega-watt solar array providing renewable energy to feed the facility’s electrical grid to charge their equipment. In 2024, we replaced 12 diesel hostlers with zero-emissions battery-electric hostlers in our San Bernardino intermodal facility. Over five years, we estimate this replacement will reduce 29.5 tons of nitrogen oxides (NOx), 4.3 tons of fine particulate matter (PM2.5), and 3,328 tons of CO2e.
Sustainable Development
Our Commitment to Our Climate and Communities
Sustainable development is a cornerstone of our sustainability strategy. As a growing railroad, we are focused on developing our operations sustainably with respect to the environment, the communities in which we live and operate and our business. In 2023, BNSF executed a deep dive into our development project processes and established a company-specific playbook. The playbook encompasses the complete process of a BNSF project, from project planning, site selection, design and construction to operation and maintenance. We measure sustainable development throughout the project by its impact on and by the community, project management, efficient resource allocation, natural world conservation, and climate and resiliency. The vision for our playbook is for BNSF project owners and teams to develop sites that provide business value while minimizing environmental impacts and improving community engagement.
- Community
- Project management
- Efficient resource allocation
- Natural world conservation
- Climate and resiliency
In 2024, BNSF focused on awareness through virtual training and in-person workshops covering sustainability topics across our network to promote implementation of the playbook. We continue to work to identify areas of efficiency and opportunity and integrate sustainability measures in current processes and planning.

Recycling & Other Sustainability Initiatives
BNSF engages in an intensive recycling program. Materials recycled in 2024 included approximately:

Additionally, we are working to do more with less by finding ways to recycle materials as we expand our facilities. We were able to recycle 37,500 tons of concrete throughout the Cicero Freight House Demo and Intermodal Facility Expansion. We also recycled 3.9 million plastic bags as part of the multi-year San Bernardino Asphalt Project.
The actions we took at San Bernardino allowed us to reduce overall construction traffic by 1,643 trips, contributing to the avoidance of 39% total reduced project emissions. Our work at Cicero allowed us to avoid 592 metric tons (CO₂) emissions through reduced trucking.

Other sustainability initiatives include:
- Responsible Care Management System: A rail carrier partnership, which promotes continuous environmental, health, safety and security improvement.
- Operation Clean Sweep: Which focuses on prevention of plastic spills.
- The Cyclyx Coalition: Which aims to build supply chains and support technologies to recycle up to 90% of U.S. plastic.
Prioritizing Conservation
BNSF is a champion of conservation. For development projects, natural world conservation is stressed throughout our sustainable development playbook, which recommends project teams look for opportunities to minimize our impacts to natural resources, such as rivers and streams, endangered species habitats and wetlands in watersheds during site-location, site layout and design of development projects. Well-informed site selection allows projects to screen potential environmental permitting requirements and potentially avoid any sensitive or protected areas.
We aim to optimize the site layout of every project by working with engineering and environmental professionals to develop operational areas and provide prompt service to our customers strategically and efficiently.
Also, we continue to work closely with partners such as the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation (NFWF) and PNW tribal governments to promote conservation projects. Our ongoing work with the NFWF supports conservation projects by reducing impacts to wildlife across the BNSF system.
In 2024, to protect wildlife and prevent flooding, we worked with the U.S. Department of Agriculture to move beavers from culverts along our railroad right-of-way in northern Minnesota to safer environments.

Investing in Remediation
We actively address environmental impacts at legacy sites – locations where predecessor railroads and others may have conducted operations for up to a century. In the last decade, we have rehabilitated approximately 100 sites and invested approximately $230 million toward remediation efforts.

Pursuing Sustainable Operations
BNSF manages our commitment to pollution prevention and environmental stewardship through our Sustainable Operations Program (SOP).
Through the SOP, we provide the BNSF team guidance and best management practices in areas including:
- Fueling
- Maintenance
- Wastewater
- Stormwater
- Waste Management
- Equipment/Materials Storage
- Property Operations & Maintenance
- Contractor/Leased Operations
- Construction and Expansion Activities
- Transportation Operations
- Adjacent Sensitive Receptors
- Agency/Community Involvement
